Every woman shall understand and know about cervical cancer cervix. Cancer cervix has claimed many lives of women around the world. Its presence in a vital part of a woman's body, sometimes making many women ashamed to see her let alone having to deal with a male doctor.
There are two types of cervical cancer, cervix, which is as follows.
Cervical cancer cervical squamous cell carcinoma, which originated or derived from cells lining the cervical mucus membranes, particularly the border endocervical and ektoserviks.
Cervical cancer, cervical adenocarcinoma, derived from epithelial cells endocervical mucus-producing glands.
Bleeding touch (contact bleeding).
In women who are still having menstrual bleeding in between menstrual cycles 2.
In the post-menopausal women vaginal bleeding or spotting.
In women over the age of 40 years bleeding very long, heavy, and often.
- Pelvic pain, back or leg.
- From the vagina out of urine or feces.
- Broken bones (fractures) due to spread of cancer cells.
The first sexual activity is less than 18 years (married young.)
System resistance decreases.
Many sexual partners.
Smoking.
Bad hygiene.
Infection: GO, syphilis, HIV / AIDS, chlamydia.
Many children.
Pap-Smear-also for early detection
Colposcopy
Biopsy
The usual treatment is that the patient should continue to check the existence of the cervical cervical cancer, depending on the type and location of cancer. Because cervical cancer is cervical down enough to make the sufferer physically and mentally, then it is necessary for the patient's family to provide encouragement and support so people do not feel alone in the face of illness. Nutrition and proper nutrition is needed by the patient to the treatment process takes place smoothly.
Use condoms for high-risk groups
Do not smoke
Single-faithful spouse on spouse
Reducing sexual activity
Maintain cleanliness
Healthy living behavior
Anti-HPV vaccination
As for the early detection could by doing regular pap-smear.
In general, people come to the doctor (known to suffer from cancer) is in an advanced stage.
Pap-smear done regularly can help find. Early changes in cervical cells before they become cancerous.
Early changes (precancerous) can be treated easily, are when it became difficult to cancer treatment.
Though women are not sexually active, including those who have menopause, because the risk of cervical cancer increases with age.
Women who underwent partial removal of the uterus or the cervix intact.
Maternity home
Place practices obstetrics-gynecology specialists, general practitioners and midwives who have been trained
Bureau of cancer consultation
Pap-smear result is complete and can be taken approximately 1 week.
The HPV virus transmission through sexual intercourse in general. Based on the data obtained, about 500 thousand women die per year due to cervical cancer cervix. HPV genome consists of transcription elements (E1, 2,4,5,6,7) which has properties of oncogenes and L1 and L2 capsid which will form the immunogenic properties. HPV is classified into low-risk HPV (6, 11) and high risk (16, 18, 34, 35, 56, 58, 59, 73, and so on).
Potentially lead to high risk cervical cancer cervix because approximately 80% of HPV DNA found that the type 16 and type 18. Meanwhile, type 6 and type 11 cause warts (genital warts or condyloma accuminatum). The development of cervical cancer is cervical progressive nature, but HPV infection can occur in the early stages of spontaneous regression. Now, if a woman is exposed to infection by the HPV virus, vaccination is often used to prevent the development of cervical cancer cervix.
Age group 11-12 years
Age group 13-15 years
Age group 16-25 years
Age group 22-55 years.
Outside the earlier grouping, can be classified from women attending child health facility or obstetrics and gynecology. Meanwhile, checks the identification of DNA (hybrid capture) are not needed before vaccination for cervical cancer cervix.
Where to get vaccinated? Vaccination for prevention of cervical cancer in the cervix can be done obstetricians, pediatricians (child age group), or can also be a general practitioner. For the cost of this vaccination can be quite expensive, which is 1 vaccination series (three injections, months 0, 1, and 6), will cost about 3 million more.
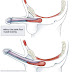
What Is Cervical Cancer Cervix?
Cervical cancer is a malignant tumor of the cervix that grow on the cervix / cervix (the lowest part of the uterus is attached to the top of the vagina).There are two types of cervical cancer, cervix, which is as follows.
Cervical cancer cervical squamous cell carcinoma, which originated or derived from cells lining the cervical mucus membranes, particularly the border endocervical and ektoserviks.
Cervical cancer, cervical adenocarcinoma, derived from epithelial cells endocervical mucus-producing glands.
Are there any signs that would be dangerous If It Regarding Cervical Cancer Cervical?
Cervical cancer cervix at an early stage often has no symptoms or signs typical. Patients with cervical cervical cancer is still able to perform daily activities, such as child care, washing, cooking or working in the office, in the factory, and so on. Sometimes some are experiencing symptoms of vaginal discharge or bleeding after intercourse.Type Symptoms of Cervical Cancer Cervical?
Increasingly whitish odorless.Bleeding touch (contact bleeding).
In women who are still having menstrual bleeding in between menstrual cycles 2.
In the post-menopausal women vaginal bleeding or spotting.
In women over the age of 40 years bleeding very long, heavy, and often.
What about Cervical Cancer Symptoms Cervical in Advanced Stage?
- Decreased appetite, weight loss, fatigue.- Pelvic pain, back or leg.
- From the vagina out of urine or feces.
- Broken bones (fractures) due to spread of cancer cells.
What Causes and Risk Factors for Cervical Cancer Cervical?
The main cause of cervical cancer is cervical infection with HPV (human papilloma virus). The risk factors for cervical cancer cervix is as follows.The first sexual activity is less than 18 years (married young.)
System resistance decreases.
Many sexual partners.
Smoking.
Bad hygiene.
Infection: GO, syphilis, HIV / AIDS, chlamydia.
Many children.
How to Diagnose Cervical Cancer Cervical?
Hip examinationPap-Smear-also for early detection
Colposcopy
Biopsy
The usual treatment is that the patient should continue to check the existence of the cervical cervical cancer, depending on the type and location of cancer. Because cervical cancer is cervical down enough to make the sufferer physically and mentally, then it is necessary for the patient's family to provide encouragement and support so people do not feel alone in the face of illness. Nutrition and proper nutrition is needed by the patient to the treatment process takes place smoothly.
Is There Any Way to Prevent Cervical Cancer and Cervical Early Detection?
To reduce the risk factors of cervical cancers in the cervix that can be done is as follows.Use condoms for high-risk groups
Do not smoke
Single-faithful spouse on spouse
Reducing sexual activity
Maintain cleanliness
Healthy living behavior
Anti-HPV vaccination
As for the early detection could by doing regular pap-smear.
Cervical Cervical Cancer - What Is a Pap-smear?
Pap-smear is a screening test (screening) to find changes in malignancy (cancer) / cervical precancer as early as possible. You do this by taking the cervical mucous membrane cells, and then sent to a pathology lab to be checked for any abnormalities or not. Pap-smear done when not needed medication or anesthesia.Cervical Cancer Cervical - Why Must a Pap-smear?
The incidence of cervical cancer in Indonesia is still high (numbers 1-2).In general, people come to the doctor (known to suffer from cancer) is in an advanced stage.
Pap-smear done regularly can help find. Early changes in cervical cells before they become cancerous.
Early changes (precancerous) can be treated easily, are when it became difficult to cancer treatment.
Cervical Cancer Cervical - Who Should Pap-smear?
Women who are over 30 years old and already had sex.Though women are not sexually active, including those who have menopause, because the risk of cervical cancer increases with age.
Women who underwent partial removal of the uterus or the cervix intact.
Cervical Cancer Cervical - Where Pap-smear Can Do?
HospitalMaternity home
Place practices obstetrics-gynecology specialists, general practitioners and midwives who have been trained
Bureau of cancer consultation
Pap-smear result is complete and can be taken approximately 1 week.
Vaccine for Cervical Cancer Cervical
Cervical cancer is a malignancy of the cervix most experienced women. As was mentioned earlier that 98% of the causes of cervical cancer is cervical Human Papilloma Virus (HPV). Of a number of types of HPV, type 16 and type 18 is a major cause of cervical cancer cervix.The HPV virus transmission through sexual intercourse in general. Based on the data obtained, about 500 thousand women die per year due to cervical cancer cervix. HPV genome consists of transcription elements (E1, 2,4,5,6,7) which has properties of oncogenes and L1 and L2 capsid which will form the immunogenic properties. HPV is classified into low-risk HPV (6, 11) and high risk (16, 18, 34, 35, 56, 58, 59, 73, and so on).
Potentially lead to high risk cervical cancer cervix because approximately 80% of HPV DNA found that the type 16 and type 18. Meanwhile, type 6 and type 11 cause warts (genital warts or condyloma accuminatum). The development of cervical cancer is cervical progressive nature, but HPV infection can occur in the early stages of spontaneous regression. Now, if a woman is exposed to infection by the HPV virus, vaccination is often used to prevent the development of cervical cancer cervix.
Cervical Cancer Cervical - Age How Vaccinations Begin?
Normally, a vaccine to prevent cervical cancer Cervical given to women aged 11-26 years. The following groupings.Age group 11-12 years
Age group 13-15 years
Age group 16-25 years
Age group 22-55 years.
Outside the earlier grouping, can be classified from women attending child health facility or obstetrics and gynecology. Meanwhile, checks the identification of DNA (hybrid capture) are not needed before vaccination for cervical cancer cervix.
Cervical Cancer Cervical - How much time Vaccination?
Vaccine for cervical cancer Cervical given in 0.1 and pad the sixth month. Women who have a history of HPV infection or precancerous lesions can be given even less effectiveness. Pregnant and lactating women are not advised to vaccinate. Vaccination is only aimed at the prevention of cervical cancer cervix is not for treatment.Where to get vaccinated? Vaccination for prevention of cervical cancer in the cervix can be done obstetricians, pediatricians (child age group), or can also be a general practitioner. For the cost of this vaccination can be quite expensive, which is 1 vaccination series (three injections, months 0, 1, and 6), will cost about 3 million more.
FAQ Cervical Cancer
4/
5
Oleh
lian