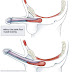
Blood pressure and cholesterol levels are generally used as an indicator to measure the risk of heart attack and stroke. But according to a new study, measured the levels of calcium in the arteries may be a better indicator.
The study said, the traditional way of measuring the blood pressure and cholesterol can give erroneous results that often patients get unnecessary prescriptions, for example, cholesterol-lowering statin drugs. This means that many people with heart attack and stroke risk low but still taking medications they do not really need.
In contrast, the study said, the savings in the artery calcium detected in CT scans can provide more accurate results. According to the researchers, people with little or no savings calcium in the arteries, heart attack and stroke risk is very small.
Because of the small risk, the researchers argue, these people just need a change of lifestyle advice, but do not need to take medication on a regular basis.
The calcium present in the arteries can lead to calcified plaque. This can result in hardening of the arteries which became one of the triggers of heart attacks.
The findings of a recent study published in the European Heart Journal was believed that calcium scanning adds to the evidence in the blood vessels as a way to predict the risk of heart attack.
The study involved nearly 7,000 participants who had been through the measurement of the risk of a heart attack in the traditional manner with cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and lifestyle. They also underwent artery calcium scanning. Then, they were followed for seven years.
Researchers study Roger Blumenthal, professor of medicine and director of the Johns Hopkins Ciccarone Center said 15 percent of people who otherwise have little risk of heart attack and turns the traditional measurement to get a high score for the content of calcium in the blood vessels. And the result, after followed for seven years, they are high risk.
" On the other hand, 35 percent of participants who expressed a high risk and should be taking drugs such as aspirin and statins do not have calcium in their arteries. They are very small risk result after seven years, " he said.
The study said, the traditional way of measuring the blood pressure and cholesterol can give erroneous results that often patients get unnecessary prescriptions, for example, cholesterol-lowering statin drugs. This means that many people with heart attack and stroke risk low but still taking medications they do not really need.
In contrast, the study said, the savings in the artery calcium detected in CT scans can provide more accurate results. According to the researchers, people with little or no savings calcium in the arteries, heart attack and stroke risk is very small.
Because of the small risk, the researchers argue, these people just need a change of lifestyle advice, but do not need to take medication on a regular basis.
The calcium present in the arteries can lead to calcified plaque. This can result in hardening of the arteries which became one of the triggers of heart attacks.
The findings of a recent study published in the European Heart Journal was believed that calcium scanning adds to the evidence in the blood vessels as a way to predict the risk of heart attack.
The study involved nearly 7,000 participants who had been through the measurement of the risk of a heart attack in the traditional manner with cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and lifestyle. They also underwent artery calcium scanning. Then, they were followed for seven years.
Researchers study Roger Blumenthal, professor of medicine and director of the Johns Hopkins Ciccarone Center said 15 percent of people who otherwise have little risk of heart attack and turns the traditional measurement to get a high score for the content of calcium in the blood vessels. And the result, after followed for seven years, they are high risk.
" On the other hand, 35 percent of participants who expressed a high risk and should be taking drugs such as aspirin and statins do not have calcium in their arteries. They are very small risk result after seven years, " he said.
Measure Levels of Calcium Prevent Heart Attack and Stroke
4/
5
Oleh
lian