Pathophysiology of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease AKA COPD
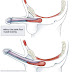
COPD COPD Lung Normal Lung Pathophysiology of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
The pathophysiology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is primarily a change in the airway, but there may also be changes in pulmonary parenchymal tissue and pulmonary vasculature. Most cases of COPD are caused by exposure to harmful substances, most often caused by cigarette smoke. The pathophysiologic mechanism remains unclear, but is thought to be caused by many factors.
In comparison, inflammation in asthma is characterized by elevated CD4 lymphocyte T cells, eosinophil and interleukin (IL) -4 and IL-5. However this can not be used for diagnosis, because there are conditions of asthma that develop into COPD.
1. Centracinar
Characterized by damage to the bronchioles and central parts of the acini. This type of emphysema is usually found in smokers and the upper lobe is the most severely damaged part.
2. Panacinar
Characterized by extensive damage to all parts of the acinus. This type usually causes severe damage to the lower lobe and is usually found in patients with alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency.
3. Distal Acinar
Damage occurs in the distal structures of the airway, ductus and alveolar saccus. This type of emphysema is localized to septa fibrous or pleura and will lead to bullae formation. A ruptured apical bullae can cause spontaneous pneumothorax.
Pulmonary vascular damage
Changes in pulmonary vascular hyperplasia of intima tunica and smooth muscle due to chronic vasoconstriction of small pulmonary arteries triggered by hypoxia. [1, 2]
Reference
1. UpToDate. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Definition, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and staging. February 2017 [Cited 2017 14 March]; Available from: http://www.uptodate.com/contents/chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease-definition-clinical-manifestations-diagnosis-and-staging
2. MedScape. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). March 2017 [ Cited 2017 14 March]; Available from : http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/297664
Damage to the Respiratory Tract
Structural alterations of the airway are atrophy, squamous cell metaplasia, ciliary abnormalities, plain muscle cell hyperplasia, mucosal gland hyperplasia, inflammation and bronchial wall thickening. Chronic inflammation in chronic bronchitis and emphysema is characterized by an increase in the number of CD8 T-lymphocytes, neutrophils, and monocytes / macrophages.In comparison, inflammation in asthma is characterized by elevated CD4 lymphocyte T cells, eosinophil and interleukin (IL) -4 and IL-5. However this can not be used for diagnosis, because there are conditions of asthma that develop into COPD.
Lung Parenchymal Damage
Emphysema causes damage to the distal structure of the terminal bronchioles. This structure consists of bronchioles, ductus alveoulus, and saccus alveoli which are overall called asinus. Damage to the alveoli will cause air flow disruption through two mechanisms, namely by decreasing the elasticity of the airway wall and airway narrowing. There are 3 patterns of morphologic Emphysema, namely:1. Centracinar
Characterized by damage to the bronchioles and central parts of the acini. This type of emphysema is usually found in smokers and the upper lobe is the most severely damaged part.
2. Panacinar
Characterized by extensive damage to all parts of the acinus. This type usually causes severe damage to the lower lobe and is usually found in patients with alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency.
3. Distal Acinar
Damage occurs in the distal structures of the airway, ductus and alveolar saccus. This type of emphysema is localized to septa fibrous or pleura and will lead to bullae formation. A ruptured apical bullae can cause spontaneous pneumothorax.
Pulmonary vascular damage
Changes in pulmonary vascular hyperplasia of intima tunica and smooth muscle due to chronic vasoconstriction of small pulmonary arteries triggered by hypoxia. [1, 2]
Reference
1. UpToDate. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Definition, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and staging. February 2017 [Cited 2017 14 March]; Available from: http://www.uptodate.com/contents/chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease-definition-clinical-manifestations-diagnosis-and-staging
2. MedScape. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). March 2017 [ Cited 2017 14 March]; Available from : http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/297664